Antibody validation Practical guide to finding and validating suitable antibodies for research
Example step 2 Describes the retrieval of information to identify antibodies recognising PIM2 antibodies
2.A Review the published peer-reviewed literature
Reviewing the published literature is an essential step that provides an overview of the possible sub-cellular localization (nuclear, cytoplasmic, membrane etc) and tissue distribution of the target protein. The information obtained on the sequence and structure of the target can help predict not only its expected molecular weight but also the presence of post-translational modifications or splice variants. The existence of multiple forms of the protein means that an antibody may be specific for the antigen but detects multiple forms of the protein on western blotting. Although transcript expression may not always translate into actual protein expression, in the absence of protein information then RNA transcripts may provide important data suggestive of the possible distribution of its encoded protein. Studying the literature is also fundamental to the selection of positive and negative controls for your validation experiments.
The following sources of information are recommended:
i) PubMed
Is a free search engine accessing primarily the MEDLINE database of references and abstracts on life sciences and biomedical topics. Currently there are several publications describing the expression of PIM2 protein in tissue and cell line. We have selected one of them as an example.
Working example: PIM2 protein distribution
Gómez-Abad C et al. described the expression of the PIM2 protein in B-cell Lymphoma using a monoclonal PIM2 antibody clone D2D1. The authors examined PIM2 protein expression by immunohistochemistry in an independent series of 176 homogeneously treated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients, 74 of whom had a germinal centre B-cell-like phenotype (GC) and 102 activated B-cell-like (ABC) phenotype, DLBLC –derived cells lines and in reactive lymphoid tissue.

Figure legend PIM2 expression in human DLBCL samples and cell lines. Immunoperoxidase labelling of reactive tonsil showed PIM2 expression to be restricted to a small subset of GC B cells, mainly centrocytes and plasma cells (A and B). Of interest was the demonstration of PIM2-negative and PIM2-positive cases of DLBCL (C and D). Western blot analysis (E) and qRT-PCR (F) showed PIM2 protein and transcripts, respectively, in HBL-1, HLY-1, OCI-Ly3 and OCI-Ly10 cell lines, all of which have characteristics of ABC DLBC . No significant amounts of PIM2 protein or transcripts were detected in the GC-derived OCI-ly19, SUDHL-4 and SUDHL-6 DLBCL cell lines. Tubulin was used as a loading control in E).
ii) CiteAb
Is a search engine that ranks antibodies by citations, making it possible for researchers to find antibodies that have been successfully used. Please remember that some well-validated Abs are published but are not commercially available and thus will not be identified using the CiteAb search engine.
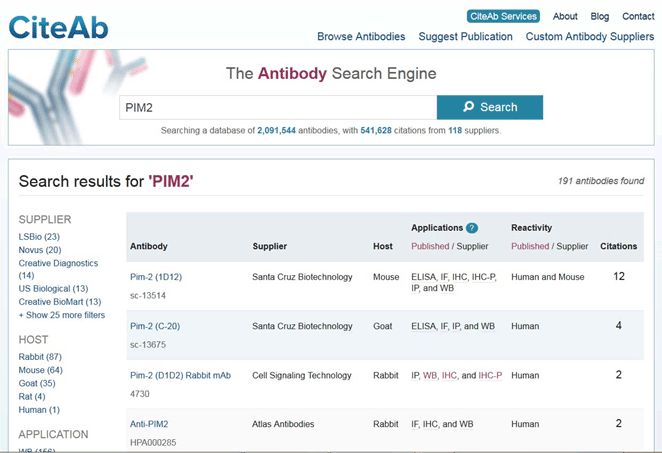
Figure legend Comparison of anti-PIM2 reagents using the CiteAb website. The PIM2 antibody D1D2 was found to have the most citations. The accompanying PIM2 citations are listed in the webpage, so the data contained within the publications can also be checked.
iii) Transcript expression
If, no antibody against the antigen of interest has been previously described, then a search needs to be made to obtain maximum information related to its gene expression at the transcript level. In most cases such information from normal human and murine tissues and human tumours can be obtained from useful tools (such as BioGps). This can, in combination with the published literature, provide relevant data concerning the transcript distribution encoding your target antigen in tissues or cell lines.
Working example: PIM2 transcript expression
Although antibodies targeting PIM2 are available, the PIM2 BioGPS profile shown below provides an example of the value of transcript information.
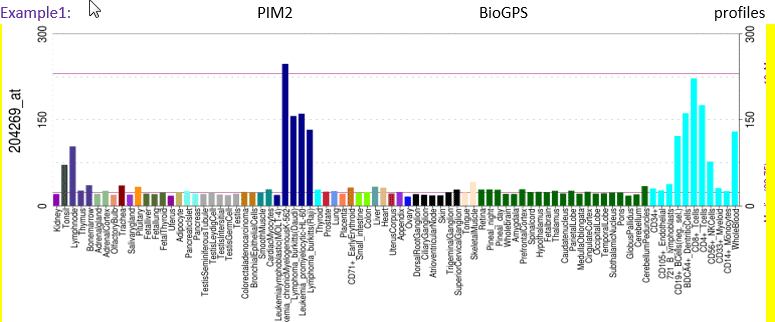
Figure legend The BioGPS diagram showing PIM2 mRNA expression in tonsil, lymph node, leucocytes and leukaemia- and lymphoma-derived cell lines. In this case the PIM2 transcripts are in keeping with the protein expression detected by the PIM2 antibody clone D2D1 previously described, It is important, however, to remember that the transcript data presented in these databases are mRNA levels, which do not always directly correspond to the quantity off protein being expressed. Furthermore, the probes used to detect gene expression may not distinguish alternatively spliced isoforms, which may exhibit different expression patterns.
2.B Find existing antibodies
There are several search engines that will help you to identify commercially available antibodies to your target antigen. The clone name of the individual antibodies should be checked since the same product can be sold under many different suppliers. The search can be further narrowed down by selecting the application intended for the antibody. Please remember that in the majority of cases, antibodies will not have been tested in all applications. Thus an antibody may not be recommended simply because it has not been tested in that specific application.
Working example: PIM2 antibody availability
The Biocompare search engine is a good example of a website providing information on available antibodies.

Figure legend Part of a search for PIM2 antibodies using the Biocompare website. This website identified 28 suppliers and a total of 185 products advertised as recognising PIM2.
2.C Review product information
The product sheets provided on the individual antibody webpages are an important source of information.
Working example: PIM2 antibody selection
A search of the published literature, relevant databases and product information resulted in the selection of three PIM2 antibodies described as recognising PIM2. The relevant information is summarized in the table below.
| Antibody clone name CHU61B | Polyclonal from Sigma | Antibody clone name D1D2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antigen use for Ab production | Not available |
SGALLHDEPYTDFDGTRVYSPP
EWISRHQYHALPATVWSLGILL
YDMVCGDIPFERDQEILEAELH
FPAHVSPDCCALIRRCLAPKPS
SRPSLEEILLDPWMQTPAEDVP
LNPSKGGPAPLAWSL
|
CALIRRCIAPKPS synthetic peptide |
| Monoclonal & Polyclonal | Mouse monoclonal | Polyclonal | Rabbit monoclonal |
| Clone name | CHU61B | Not available | D1D2 |
| Isotype | IgG2a | IgG | |
| Host species | Mouse | Rabbit | Rabbit |
| Species reactivity | Human | Not available | Human |
| Tested applications | ELISA, WB, IHC | IHC | WB and IP |
Figure legend Summary of the characteristics of three antibodies, CHU61B, D1D2 (both monoclonals) and a polyclonal antibody, described as recognising PIM2 protein.
